Hairy silica nanosphere supported metal nanoparticles for reductive degradation of dye pollutants
Xin Chen,a Li Zhang,a Bin Xu,b Tingting Chen,a Lianhong Hu,a Wei Yao,a Mengxiang Zhoua and Hui Xu *a
a Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 211816, China. E-mail: ias_hxu@njtech.edu.cn
b Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, Nanjing 210042, China
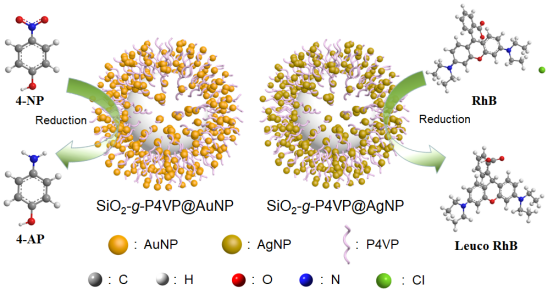
Abstract: Hairy materials can act as a sort of scaffold for the fabrication of functional hybrid composites. In this work, silica nanospheres modified with covalently grafted poly(4-vinylpyridine) (P4VP) brushes, namely, “hairy” silica spheres, were utilized as a support for the anchorage of metal nanoparticles (MNPs), thus resulting in the hierarchical SiO2@P4VP/MNP structure. In this triple-phase boundary heteronanostructure, the SiO2-supported MNPs are well stabilized by the P4VP matrix to avoid aggregation and leaching. These SiO2@P4VP/MNP nanocomposites exhibit good catalytic activity in the reductive degradation of organic dyes, i.e., 4-nitrophenol and rhodamine B and possess excellent stability and recyclability for five successive cycles.
Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 2879–2886 影响因子:4.553
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NA00020A
