Effect of Coking and Propylene Adsorption on Enhanced Stability for Co2+-Catalyzed Propane Dehydrogenation
Yihu Dai*,a, Yue Wua, Hua Daia, Xing Gaoa, Suyang Tiana, Jingjing Gua, Xianfeng Yib, Anmin Zhengb, Yanhui Yang*,a
aInstitute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 211816, China
bState Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
Abstract:
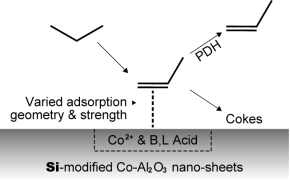
The effects of Si-additive modification on nonoxidative propane dehydrogenation (PDH) over γ-Al2O3 sheet-supported isolate Co2+ catalysts have been investigated. Si addition introduces a number of moderate-strength acid sites by the formation of composite SiAl oxides. Promoted catalytic stability is achieved on Si-modified Si-Co-Al2O3 in comparison with the Si-free Co-Al2O3 catalyst. A relatively lower graphitization degree and a higher ratio of highly reactive coke species are observed on the Si-Co-Al2O3 catalyst. The co-feeding of C3H6 significantly changes the coking reaction rates but not the coke distributions on Co-based catalysts. The interaction of C3H6 with Co catalysts can be affected by Si modification tuning the coking property and the catalytic stability of Co2+-Al2O3-based catalysts for the PDH reactions.
J. Catal. 2021, 395, 105-16.(影响因子:7.888)
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2020.12.021
