Effect of Hydrotalcites Interlayer Water on Pt-Catalyzed Aqueous-Phase Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde
Xing Gaoa, Hua Daia, Lili Penga, Di Lua, Xiaoyue Wana, Chunmei Zhoua, Jianwei Zhenga, Yihu Daia,*, Hongming Wangb,*, Yanhui Yanga,*
a Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 211816, China
b Institute of Advanced Study, College of Chemistry, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
Abstract:
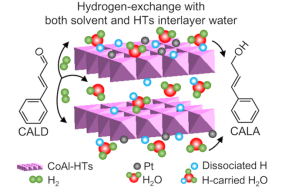
Heterogeneous hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated compounds requires understanding of the structure-activity relationship of metallic catalysts in consideration of solvent-mediated processes. CoAl hydrotalcites-supported Pt nanoparticles are employed to study the effect of solvent water and HTs interlayer water on aqueous-phase selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde (CALD). Water-mediated hydrogen-exchange pathway exists with a relatively lower-energy barrier in comparison to direct dissociation-hydrogenation pathway. The HTs interlayer water species participate in the hydrogen-exchange reaction, and also promote H2 activation and dissociation processes for accelerating the reaction even under solvent-free conditions.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2, 2516-2524.(影响因子:8.456)
论文链接: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.9b19160
